阅读感受
- 涉及生物相关的概念基本不懂
- 涉及infomation encoding&decoding的部分不太理解(涉及到SVM, ICP, GLM都不了解)
- 限于英语文献阅读能力, 可能重点没有抓住/理解错了
central nervous systems
Central nervous system (CNS) | healthdirect
Overview of the Central Nervous System (CNS) - YouTube
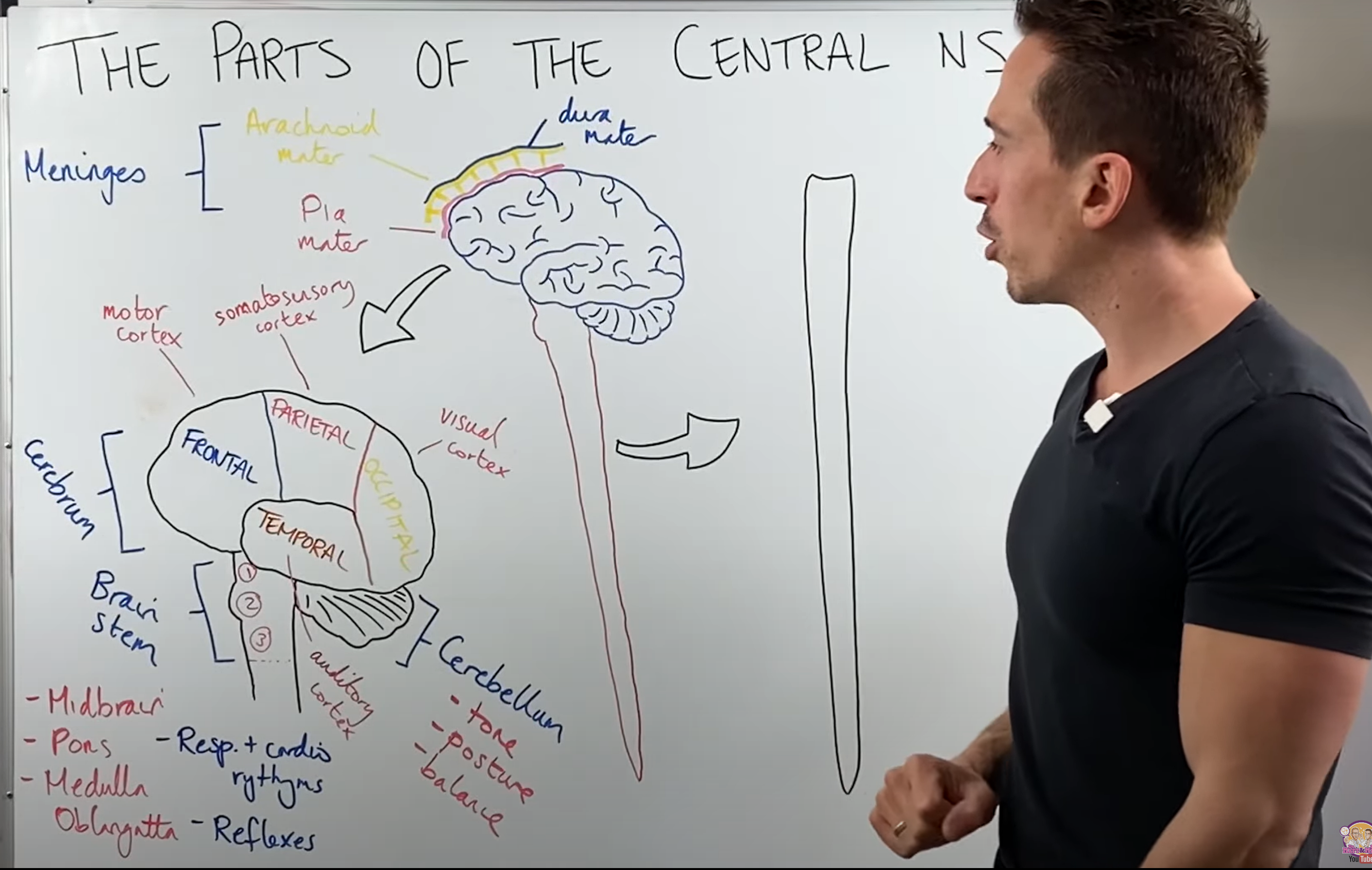
neurons
- excitable
- signal to communicate
- neurons
- muscles
- glands
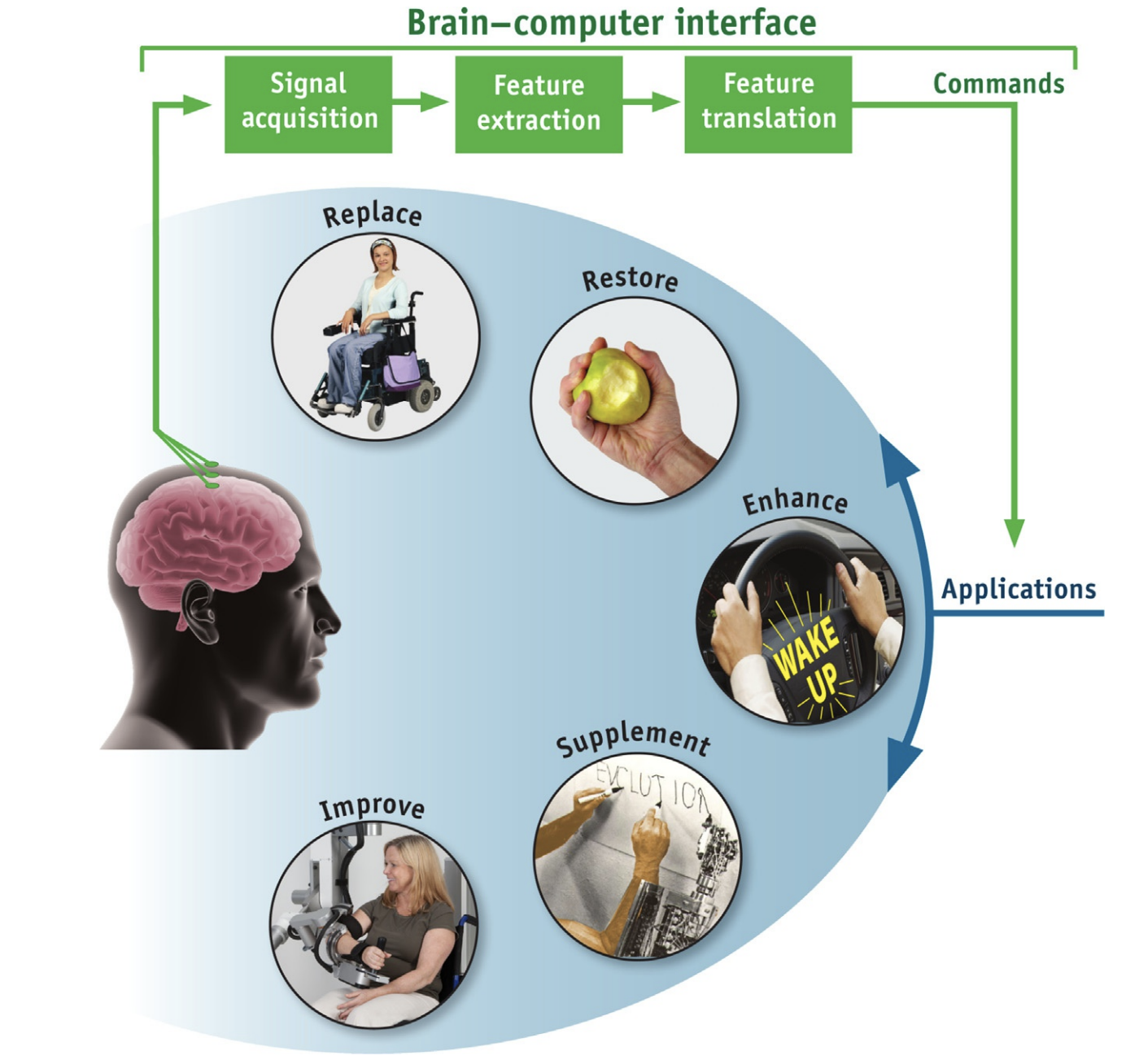
Brain-computer interfaces: Definitions and principles¶
abstract¶
- brain-computer interfaces quantify CNS acitvity and translate it into new artificial outputs that replace, restore, enhance, supplement, or improve the natural CNS outputs. -> BCIs thereby modify the interactions between the CNS and the environment.
-
source不同: spinal and brainstem motoneurons -> other CNS regions, like the sensorimotor cortex ❓
-
❗2 most difficult & critical challenge
- reliablity & accuracy
- adaptive modifications: "reliazation of this second adaptive controller, the BCI, and management of its interactions with concurrent adaptations in the CNS"
- brain areas -> by experienments
- ❗avoid mis-interpreting nonbrain signals
- goal selections with/or process control
- ❗目前进展: benefit people with neuromuscular disorders -> BCI clinical evaluation, validation, dessemination(宣传) -> requirements of clinical studies.
Definitions¶
Brain-computer interface¶
CNS outputs: neuromuscular / hormonal BCI outputs: novel, neither of these
BCI
a system that records CNS activity and translate it into artificial output that replace, restores, enhances, supplements or improves natural CNS output; it thereby modifies the interactions of the CNS with the rest of the body or with the external world.
-
foundation: sensorimotor hypothesis
graph LR; A[sensory input] --CNS--> B[motor outputs]the only function of CNS
-
signals
- 电生理信号
- 神经化学信号
- 新陈代谢现象
- 神经元的动作电位
- 突触电位?
- 神经介质的释放
- 摄氧量(VO_2, oxygen uptake)
- 电场 / 磁场, 血流量?, 血红蛋白的氧合作用(hemoglobin oxygenation)
-
replace: 重构功能
- restore: 重新建立刺激(stimulation)
- enhance
- supplement
- improve
目前进展: replace, restore > improve > enhance, supplement
- ✨ BCI changes the interactions (不能只是监控大脑活动)
related terms¶
- BCI > BMI
- dependent BCI: uses brain signals that depend on muscle activity
不仅要想, 还要动?
-
independent BCI: muscle activities are not needed for generating the brain signals that BCI measures.
只用想, 不用动. -> 对没法动的人(ALS患者)更有帮助
-
hybrid BCI
- 采用两种信号
- 将BCI输出与原先的肌肉输出合并的BCI
adaptive neurotechnologies¶
They adapt to optimize the new interaction and they often induce(诱导) adaptive plasticity in the CNS, which also helps optimize the interaction
BCI和CNS两个方面的adaptation
Key issues¶
BCIs create artificial CNS outputs¶
2 principles regarding how the CNS produces its natural outputs - creation of natual outputs is distributed throughout the CNS. (多区域协作) - the actions produced by natural CNS outputs are acquired and maintained by initial and ongoing adaptations in all the CNS regions involved. (ongoing adaptation)
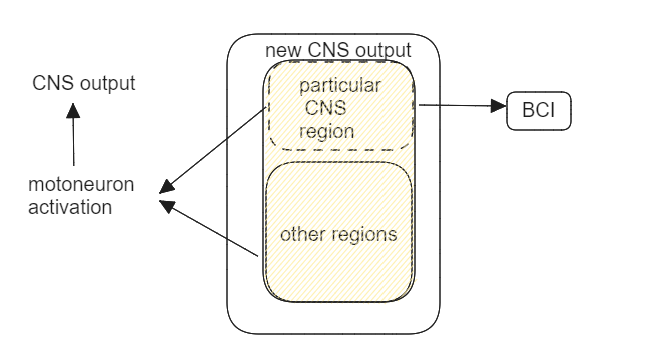
原先的某个特定的CNS区域本来是配合其他的一些区域来产生神经信号来activate 相应的spinal motoneurons从而产生CNS output(运动), 但是在BCI介入以后, 这些区域不再负责产生activation, 而是负责操控这个特定的被BCI识别信号的区域能够产生特定信号(例如操纵假肢的信号), 从而使得这个特定的区域负责产生最终的CNS output. 这个转变就是adaptation. 简单来说, 现在神经不再操控身体, 而是操控假肢.
BCI operation requires the effective interaction of two adaptive controllers¶
- trade-off: 复杂的不能长久可靠
- 2 adaptive controllers: BCI, CNS
- 信号的属性会变化
- CNS本身也会变化?
Selecting signal types and CNS regions¶
- EEG: 脑电图, 厘米级
- ECoG: 脑皮层电图, 毫米级
- neuronal action potentials: 10微米级
- 什么方法最好要按照具体情况来, 因此需要实验决定.
- best regions to record signals: sensorimotor(and visual) cortical areas (most)
note: 即便是已经失去功能多年的大脑皮层也能产生对BCI有用的信号.
Detecting and avoiding artifacts¶
BCI artifacts
They may obscure or contanminate the signals that provide output commands. - from the environment - from the body - BCI hardware
- solution for EEG-based BCI: topographical and frequency analyses to differentiate
- solution for fNIRS: 差不多的方法
- 总之, 不能只选择几个location, 或者narrow frequency band
BCI output commands can either select goals or control pocesses¶
- goal-selection BCI What to do
- puts the burden of rapid complicated interactive control on the application
- select & communicate
- 适合做比较有限的工作(不会发生意外的)
-
process-control BCI How to do
- more detailed -> more complex
-
combined BCI: 有机结合
Creating and disseminating important BCI applications¶
- ethical issues
- clinically validated BCIs
- challenge: profitable
- nonmedical BCI
- rehabilitation applications of BCI e.g. [[“卒通”脑机接口偏瘫居家康复解决方案BP.pdf]]
Real-time fMRI for brain-computer interfacing¶
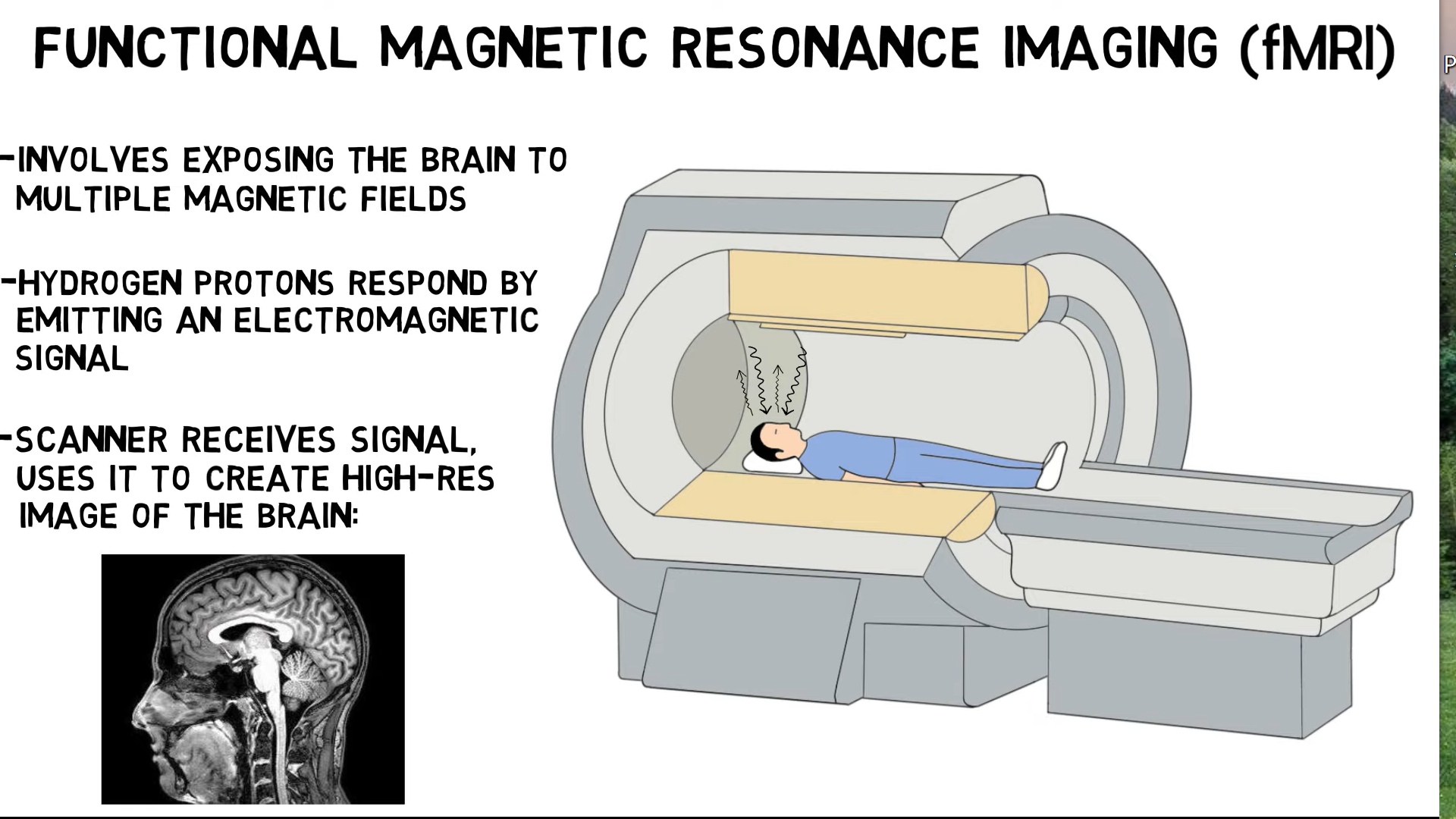
2-Minute Neuroscience: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) - YouTube The difference between functional MRI and regular MRI | Ohio State Medical Center - YouTube
Using fMRI to measure brain activation¶
advantages: - spatial resolution - the ability to reach deep subcortical(皮层下的) structures - whole-brain coverage
Phisiologic principles of fMRI¶
graph TD;
A[neuronal acitities]-->B[localized changes]-->C[concentration ratio of oxy- and deoxy- hemoglobin changes]--different magnetic properties-->D[BOLD数值的变化]
blood oxygenation level-dependent, BOLD(血氧水平依赖) hemodynamic response function HRF
fMRI的时空分辨率受到hemodynamic response分辨率的限制
1.5t / 3T -> 1-3mm & 1-3s
Measurement artifacts¶
disadvantages: image suffer from - signal dropouts (采样率的原因?) - geometric distortions
substantial head movement(显著的头部移动)
提高信噪比(signal-to-noise ratio, SNR): 采用平滑手段, 预处理
Suitability of fMRI as functional-neuroimaging methods in BCI¶
Evaluation of fMRI as BCI Method¶
- robustness
- +relatively high single-trial reliability
- +high signal-to-noise ratio
- +high spatial resolution of the BOLD signal
- +large brain coverage
- -artifacts(e.g. head motion & susceptibility artifacts)
- relatively low temporal resolution -> information transfer rate is limited
- flexibility: 目前受限, 未来实现个人化后有希望
- safety
- 非侵入式, 相对安全
- 涉及到磁场, 避免携带金属
- user friendliness: rather limited
- BCI operator: simultaneously control 3+ PCs: scanner console, stimulation PC, and real-time data analysis PC
- BCI user:
- isolated in separate scanner room -> ❌interactions between user and operator
- lying position, no moving
- scanner noise
- unpleasant side effects
- Pros: short preparation time
- costs: 贵
Methodology of fMRI-based BCI⭐¶
General aspects of information encoding and decoding in BCI¶
- 目标: "心照不宣", "读心术"
- 最显然的办法: 比较回答yes/no时的不同的神经活动 -> 目前无法分辨
- 间接的办法: people can intentionally and effectively generate differentiable brain activity/brain signals by performing different mental activities
- e.g.
encoding & decoding yes/no ↔ mental activities
graph TD; A[question]-->B["Yes"]-->D[metanlly recite a poem] A-->C["No"]-->E[imagine to spatially navigate through a house] D-->F[different brain activity patterns] E-->F
Information encoding¶
Modulation of spatial fMRI-signal features¶
amount of mental activities are limited, so far 6 at most
categories: - cognitive tasks - covert lagnuage-related tasks - imagery tasks - selective attentions tasks
temporal¶
onsets, offsets, durations不同
Magnitudinal¶
量化活动强度用于区分?
different brain-avtivation levels: up to 5
需要averaging
Combinatory¶
效果更好
Information decoding¶
Real-time fMRI analysis¶
- 实时分析: 单次的处理时间不能超过数据传输的间隔
- 增量式算法
GLM analysis?
😵没看懂
decoding based on mutiregional statistical analyses¶
Decoding based on multivoxel pattern cliassification¶
似乎与Machine Learning相关: supporter vector machine?
Current and future real-time fMRI-based BCI applications¶
- 限于前文所述的局限性, 目前对瘫痪病人的作用仅限于一些特殊情况, 但还是有价值的
- 另一用处: neurofeedback technique, promising
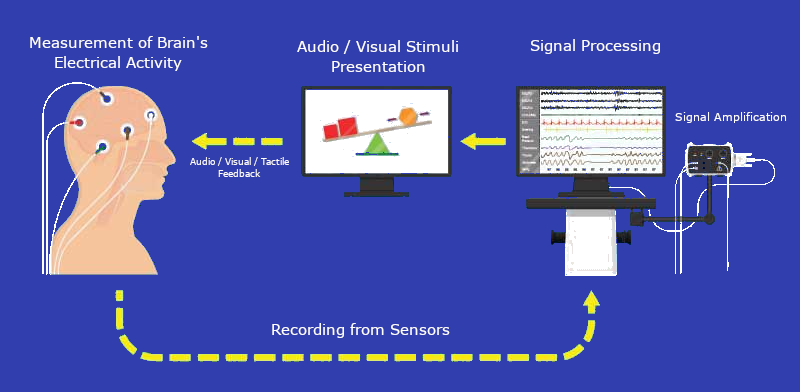
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback that focuses on the neuronal activity of the brain. The training method is based on reward learning (operant conditioning) where a real-time feedback provided to the trainee is supposed to reinforce desired brain activity or inhibit unfavorable activity patterns.
- as a neuroscientific research tool
Conclusions and future methodological perspectivfes of real-time fMRI¶
High temporal resolution¶
- cleaner signals
- shorter response delays
High-spatial resolution fMRI BCIs at ultra-high magnetic fields¶
- may allow research moving from patterns across task-related regions and networks to more fine-grained overlapping activation patterns within brain areas
- pick up weaker signals
- e.g. Letter recognition