LeetCode 刷题笔记¶
知识学习¶
C++STL容器学习¶
vector¶
- 变长数组
- 访问:下表or迭代器
- 函数:
- push_back()
- pop_back()
- size()
- clear() O(N)
- insert(it, x) O(N)
- erase(it)
- 常用函数
vector<int> a;
n = a.size();
a.resize(n);
a.assign(n, val);
string¶
- 字符串加强版,减少对指针的依赖,集成了一些操作
string str = "abcd";
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
cout << str[i];
}
cout << endl;
cin >> str;
cout << str;
string::iterator it = str.begin();
cout << *it << endl;
string str2 = "opq";
str.insert(3, str2);//输出“abcopqd”
str.insert(str.begin(), str2.begin(), str2.end());//将另一个str中的某一部分查到指定位置 末尾是指最后一个字符的下一个
str.erase(str.begin() + 4);
str.erase(str.brgin(), str.end());
str.clear();
string str1 = str2.substr(pos, len);
str1.find(str2);//寻找匹配的子串第一次出现的pos,否则返回string::npos
stack¶
queue¶
- 队列 FIFO
- 函数:
- push()
- pop()
- front() back()
- bool empty()
- size()
- 用途:BFS
- 注意点:使用 front() back() pop() 前,必须用empty()判断队列是否为空
priority_queue¶
- 优先队列 用 **堆**实现, 队首元素一定是当前队列中优先级最高的那个。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
priority_queue<int> q;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int> > q_less//less<int> 表示数字大的优先级越大,即数字越来越小
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > q_great// greater<int> 表示数字小的优先级越大,即数字越来越大
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
q.push(1);
printf("%d\n", q.top());
return 0;
}
-
注:在使用top()函数前,必须用empty()判断优先队列是否为空
set (unordered_set)¶
- set 内部==自动有序==(unordered_set不排序) 不含重复元素
- 访问 迭代器(地址)
- 函数
- insert() O(logN)
- find() O(logN)
- erase() way1: erase(it) O(1) way2: erase(value) O(logN) //也可以erase(it, st.end())实现删除一段元素
- size() O(1)
- clear() O(N)
- 主要用处:自动去重&&按升序排序
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace st;
set<int> st;
set<int>::iterator it;
for(it; it != st.begin(); it++) {
cout << *it << endl;
}
return 0;
map¶
- 映射:map可以将任何基本类型(包括STL容器)映射到任何基本类型,例如 建立string -> int 的映射
- 另一种情形:判断给定的一些数字是否在某个文件中出现过。按照正常思路,可以开一个bool类型的hashTable[max_size],但是当这些数字很大时(例如几千位)这个数组就会开不了。而这时map可以派上用场。将这些数字转换为字符串,然后建立string -> int 的映射(或是直接建立int -> int 的映射)。
- 访问:和访问普通数组是一样的。但是需要注意,map中的键是唯一的,多次的重复输入将会覆盖之前的value。也可以使用迭代器。
- map会以键从小到大的顺序自动排序(同样因为其是用红黑树实现的)
- 函数:
- find(key) O(logN) 返回地址
- erase(it) O(1) || erase(key) O(logN) || erase(first, last) 注意last为==区间末尾迭代器的下一个元素==(美国人喜欢左闭右开)
- size() O(1)
-
clear() O(N)
-
用途:任意类型映射 大整数 每个key对应的val唯一(否则用multimap)
//map<keyTypeName, valTypeName> mp;//两个类型:key -> val
map<char, int> mp;
mp['m'] = 20;
mp['r'] = 30;
mp['a'] = 40;
for(map<char, int>::iterator it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
}//输出 a 40 // m 20 // r 30
pair¶
pair<int, char> a[3];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
a[i].first = i;
a[i].second = ''
}
list¶
algorithm头文件下的常用函数¶
sort()函数的用法¶
//sort(首元素的地址, 尾元素地址的下一个地址, 比较函数(非必填))
/*bool cmp(比较对象元素的类型 a, b) {
return 符合排序要求的返回true;
}
*/
//对于int 类型数据的排序
int a[] = {1, 7, 8, 6, 2, 4};
sort(a, a+6, cmp_int);//默认升序
bool cmp_int(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
//对于char 类型的排序
int char s[] = {'a', 'c', 'b'};
sort(s, s+ 3, cmp_char);//默认字典序
bool cmp_char(char a, char b) {
return a > b;
}
//对于struct 的排序
typedef struct{
int a;
int b;
}stru;
stru struc[3];
//省略初始化内容
sort(struc, struc+3, cmp_struct);
bool cmp_struct(stru a, stru b) {
if(a.a != b.a) return a.a > b.a;
else return a.b > b.b;
}
//对vector<int> 的排序
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp_vector);
bool cmp_vector(int a, int b) {//注意!:因为vector中的元素类型为int
return a > b;
}
vector<vector<int> > vv;
//省略初始化
sort(vv.begin(), vv.end(), cmp_vvector);
bool vvector(vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
if(a[0] != b[0]) return a[0] > b[0];
else return a[1] > b[1];//首先以首元素排序,其次以第二元素排序
}
//对string 类型排序
string str[3] = {"bbbb", "cc", "aaa"};
sort(str, str+3, cmp_str);
bool cmp_str(string a, string b) {
return a.length() < b.length();//按字符串长度排序
}
注意:在类中定义cmp函数时要加**static**
stable_sort用法¶
stable_sort是稳定排序,而sort是不稳定排序,即相同元素的先后顺序在排序前后可能会发生变化。
- 时间复杂度:O(NlogN) \sim O(N(logN)^2)
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::stable_sort
#include <vector> // std::vector
//以普通函数的方式实现自定义排序规则
bool mycomp(int i, int j) {
return (i < j);
}
//以函数对象的方式实现自定义排序规则
class mycomp2 {
public:
bool operator() (int i, int j) {
return (i < j);
}
};
int main() {
std::vector<int> myvector{ 32, 71, 12, 45, 26, 80, 53, 33 };
//调用第一种语法格式,对 32、71、12、45 进行排序
std::stable_sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.begin() + 4); //(12 32 45 71) 26 80 53 33
//调用第二种语法格式,利用STL标准库提供的其它比较规则(比如 greater<T>)进行排序
std::stable_sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.begin() + 4, std::greater<int>()); //(71 45 32 12) 26 80 53 33
//调用第二种语法格式,通过自定义比较规则进行排序,这里也可以换成 mycomp2()
std::stable_sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), mycomp);//12 26 32 33 45 53 71 80
//输出 myvector 容器中的元素
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = myvector.begin(); it != myvector.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << *it << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
lower_bound & upper_bound()¶
-
lower_bound( )和upper_bound( )都是利用==二分查找==的方法在一个**排好序**的数组中进行查找的。
-
lower_bound( begin,end,num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于或等于num的数字,找到-返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
-
upper_bound( begin,end,num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
auto it = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), val);\\ 返回第一个大于等于val的迭代器
auto it = upper_bound(v.begin(),, v.end(), val);\\返回第一个大于val的迭代器
int a[5] = {1,3,4,2,5};
sort(a, a+5);
int idx = lower_bound(a, a+5, 3);\\返回的是下标
std::cout << idx;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100000+10;
const int INF=2*int(1e9)+10;
#define LL long long
int cmd(int a,int b){
return a>b;
}
int main(){
int num[6]={1,2,4,7,15,34};
sort(num,num+6); //按从小到大排序
int pos1=lower_bound(num,num+6,7)-num; //返回数组中第一个大于或等于被查数的值
int pos2=upper_bound(num,num+6,7)-num; //返回数组中第一个大于被查数的值
cout<<pos1<<" "<<num[pos1]<<endl;
cout<<pos2<<" "<<num[pos2]<<endl;
sort(num,num+6,cmd); //按从大到小排序
int pos3=lower_bound(num,num+6,7,greater<int>())-num; //返回数组中第一个小于或等于被查数的值
int pos4=upper_bound(num,num+6,7,greater<int>())-num; //返回数组中第一个小于被查数的值
cout<<pos3<<" "<<num[pos3]<<endl;
cout<<pos4<<" "<<num[pos4]<<endl;
return 0;
}
数据结构¶
链表¶
树¶
- 概念:node\ leaf\ edge\ child\ subtree
- 度(degree):子树的棵树//最大值为树的度
- 由于一条边连接两个节点,且树中不存在环,因此对有n个节点的树,边数一定是n - 1。且满足**连通、边数= 顶点数 - 1的结构一定是一棵树**。
- 叶子节点:度为0的节点
- 深度(depth):自顶向下 高度(height):自底向上
- 完全二叉树:满二叉树+只能是右子节点不存在
- 注意:新建树/节点后必须初始化其左右子节点的地址为NULL
树的遍历¶
-
前序遍历(preorder):根-左-右
-
判断当前节点是否为NULL
- 访问根节点
- 递归左子节点
-
递归右子节点
-
中序遍历(inorder):左-根-右
-
后序遍历(postorder):左-右-根
-
层序遍历(layerOrder):
typedef struct TreeNode TreeNode;
struct TreeNode {
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
int val;
};
queue<TreeNode *> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
TreeNode *now = q.front();
if(now->left != NULL) q.push(now->left);
if(now->right != NULL) q.push(now->right);
q.pop();
}
BST 二叉搜索树¶
- 定义:左子树上所有节点的数据域均小于或等于根节点的数据域,右子树上所有节点的数据域均大于根节点的数据域。
- 查找:有点类似二分查找:左子树<=根节点<右子树
- 插入:基于查找
- 性质:对二叉查找树进行中序遍历,遍历的结果是有序的。
AVL树 平衡二叉树¶
并查集¶
- 合并:合并两个集合,先判断是否为同一个集合,若不是,则把其中一个根节点的父节点指向另一个集合的根节点
- 查找:判断两个元素是否在同一个集合
- 代码实现:
int father[N];//father[i]表示元素i的父节点,若father[i] == i,则说明i为集合的根节点,作为所属集合的标识
//initialize
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
father[i] = i; //or father[i] = -1
}
//find
int findFather(int x) {
while(x != father[x]) {
x = father[x];
}
return x;
}
//findRecursive
int findFatherR(int x) {
if(x == father[x]) return x;
else return findFatherR(father[x]);
}
//union
void union(int a, int b) {
int faA = findFather(a);
int faB = findFather(b);
if(faA != faB) {
father[faB] = faA;
}
}
路径压缩¶
把当前查询节点的路径上的所有节点的父节点都指向根节点,使得查找时不必一直回溯,查询的复杂度可以降到O(1)。
因此转换的过程可以概括为:
- 按原先的写法获得x的根节点r
- 重新从x开始走一遍寻找根节点的过程,把路径上经过的所有节点的父节点都改为根节点。
int findFather(int x) {
int remark = x;
while(x != father[x]) {
x = father[x];
}
while(remark != father[remark]) {
int tmp = father[remark];
father[remark] = x;
remark = tmp;
}
}
字典树¶
实现前缀匹配,模糊搜索。可以快速的插入和查找
哈夫曼树(最优二叉树)¶
路径长度:从根节点出发到达该节点所经过的边数。
带权路径长度(weighed path length of tree):\sum(叶子节点的权值\times路径长度)
哈夫曼树的构建思路:每次合并节点权值最小的两个节点,合并后的节点放回,进行下一次的比较。(图示见下)
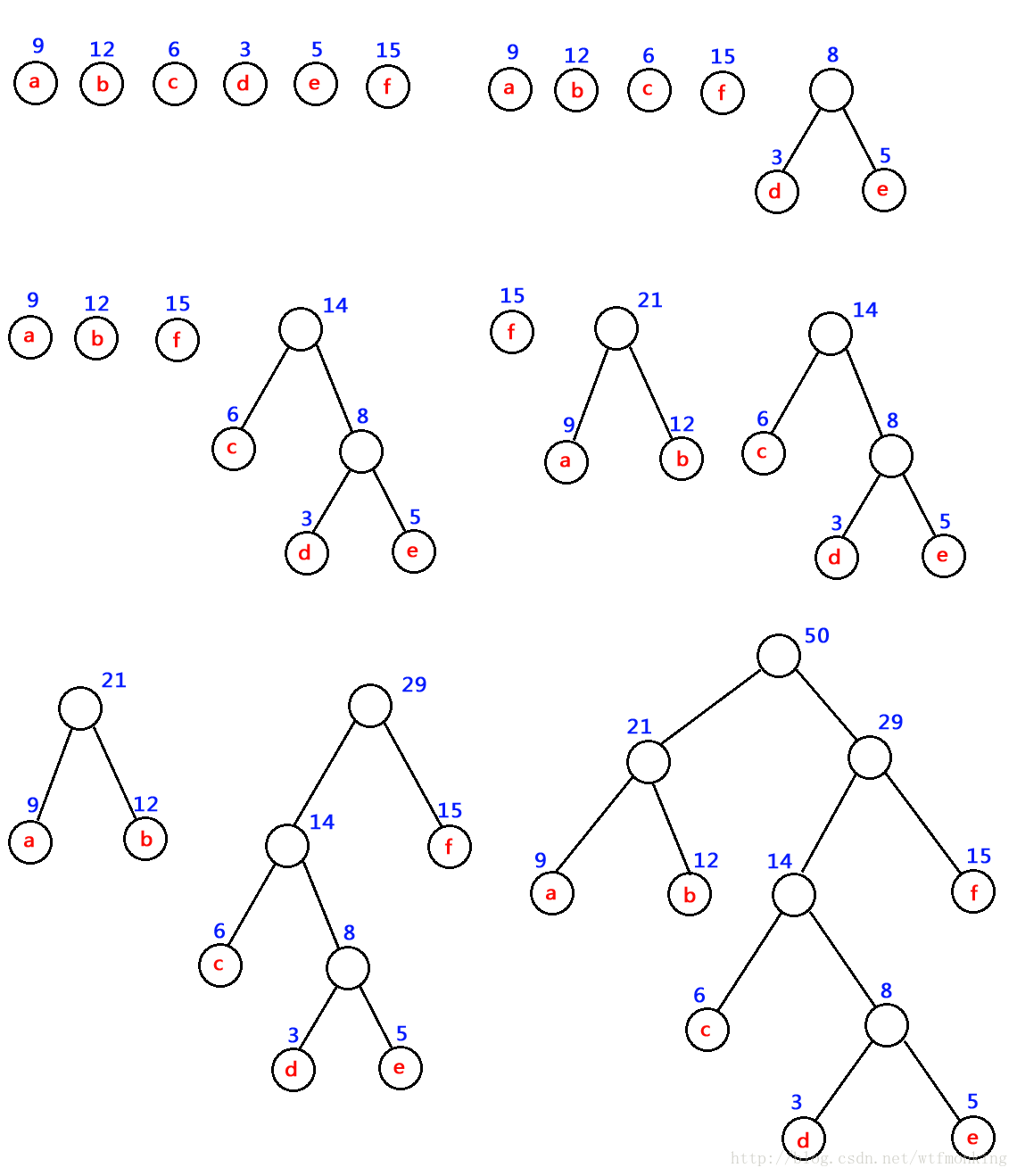
性质:哈夫曼树不存在度为1的节点,并且权值越高的节点相对来说越接近根节点。
哈夫曼编码:可变长编码 减少编码长度
栈¶
队列¶
树状数组¶
引入:考虑一个单点修改、区间求和的问题。
若采用朴素算法,
单点修改:O(1)
区间查询:O(N)
若采用前缀和,
单点修改:O(N)
区间查询:O(1)
引入树状数组,使得修改和查询的复杂度都为O(logN)
预备知识:lowbit()运算¶
非负整数 n 在二进制表示下最低位 1 及其后面的 0 构成的数值
$$
\begin{aligned}
\sim n+1=-n &(\sim \text { 表示取反 }) \
\operatorname{lowbit}(n) &=n \&(\sim n+1) \
&=n \&-n
\end{aligned}
$$
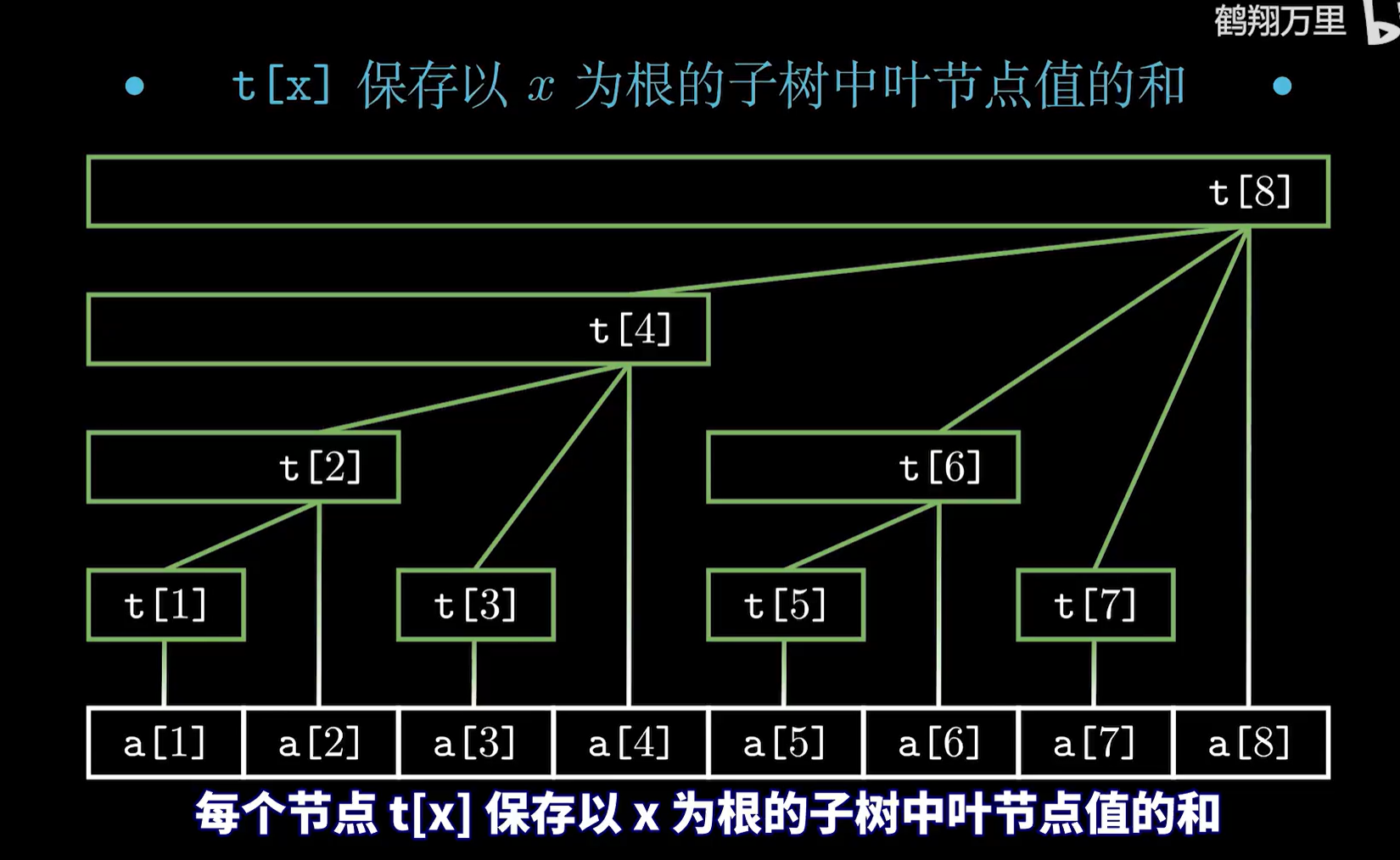
树状数组的性质
-
c[x]存储(x-lowbit(x),x]的和
-
c++ int sum = 0; for(int i = x; i > 0; i -= lowbit(i)) { sum += c[i]; }
哈希(散列)¶
- definition: Hash Table is a data structure to map key to values (also called Table or Map Abstract Data Type/ADT). It uses a hash function to map large or even non-Integer keys into a small range of Integer indices (typically [0..hash_table_size-1]).
The probability of two distinct keys colliding into the same index is relatively high and each of this potential collision needs to be resolved to maintain data integrity(数据可靠性).
There are several collision resolution strategies that will be highlighted in this visualization: Open Addressing (Linear Probing, Quadratic Probing, and Double Hashing) and Closed Addressing (Separate Chaining).
[来源](哈希表(开放寻址法:线性探测,二次探测,双倍散列 以及 闭散列分离连接法) - VisuAlgo)
-
哈希的本质是一个数组:
-
数组+链表
-
数组+BST(冲突比较多时,降低存储效率以换取查找效率)
-
哈希冲突的解决方法:
-
拉链法
-
开放寻址法
-
哈希的核心是哈希函数
-
如何理解哈希表?(hashTable)
-
例:QQ群列表里找某个人?逐个找(遍历)?太慢!
- 策略:按照昵称首字母a-z排序,例如昵称为Jack_shen的,直接在j中查找即可。
-
注意到这里我们对输入的数据(Jack_shen)进行了某种运算(取首字母),得到了对应的key(j),相当于将所有的输入的字符串分为26个堆来存放,这样查找时根据这个算法再次计算得到其所在的key,只需在这个堆中进行遍历即可。
-
键值对:一个值对应另外一个值(key -> value)key叫做键值,value叫做哈希值
-
如何理解哈希映射?(hashMap)
优先队列(堆)¶
- 优先队列(priority queue)。实现的功能就是**取出一堆数字中的最大数或者最小数**,以最小数放在堆顶为例,如果维护一个链表,那么添加元素的复杂度为O(1),但是查找元素的复杂度为O(N),我们必须遍历链表的每一个元素才可以找到其中的最小值;如果维护一个普通的单调数组,这样的话插入的复杂度为O(N),查找的复杂度为O(1),所以一种折衷的方案是使用高度平衡的二叉树,由于其结构完全确定,我们其实可以只用一个数组来储存,但并不破坏其二叉树的本质。
令数组下标从1开始,会有1|2 3|4 5 6 7|... 父节点到子节点有这样的关系: $$ root&x\ leftLeaf&2x\ rightLeaf&2x+1 $$
所以我们可以据此推断出任意一个节点的父节点和子节点。
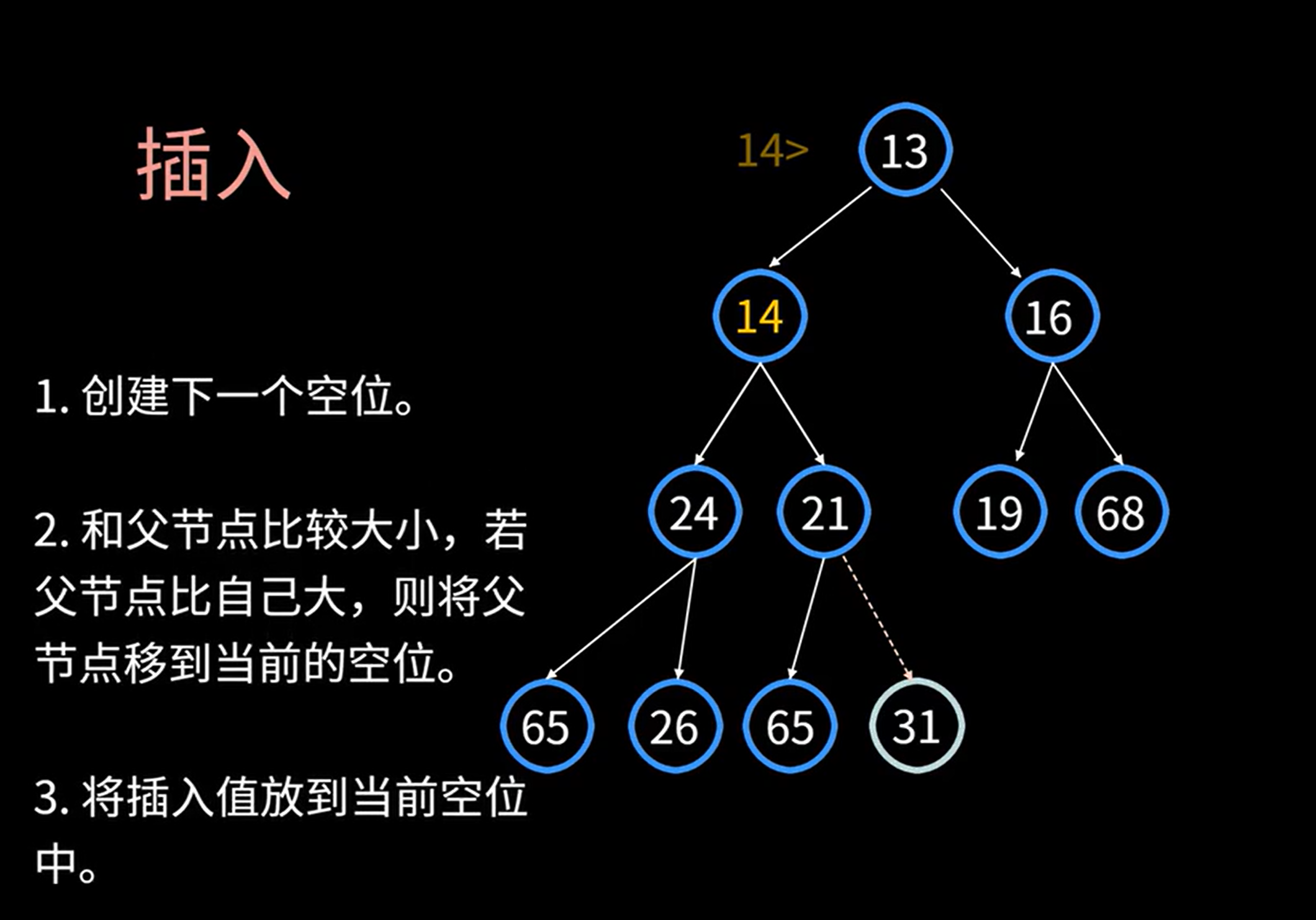
- 堆的添加元素
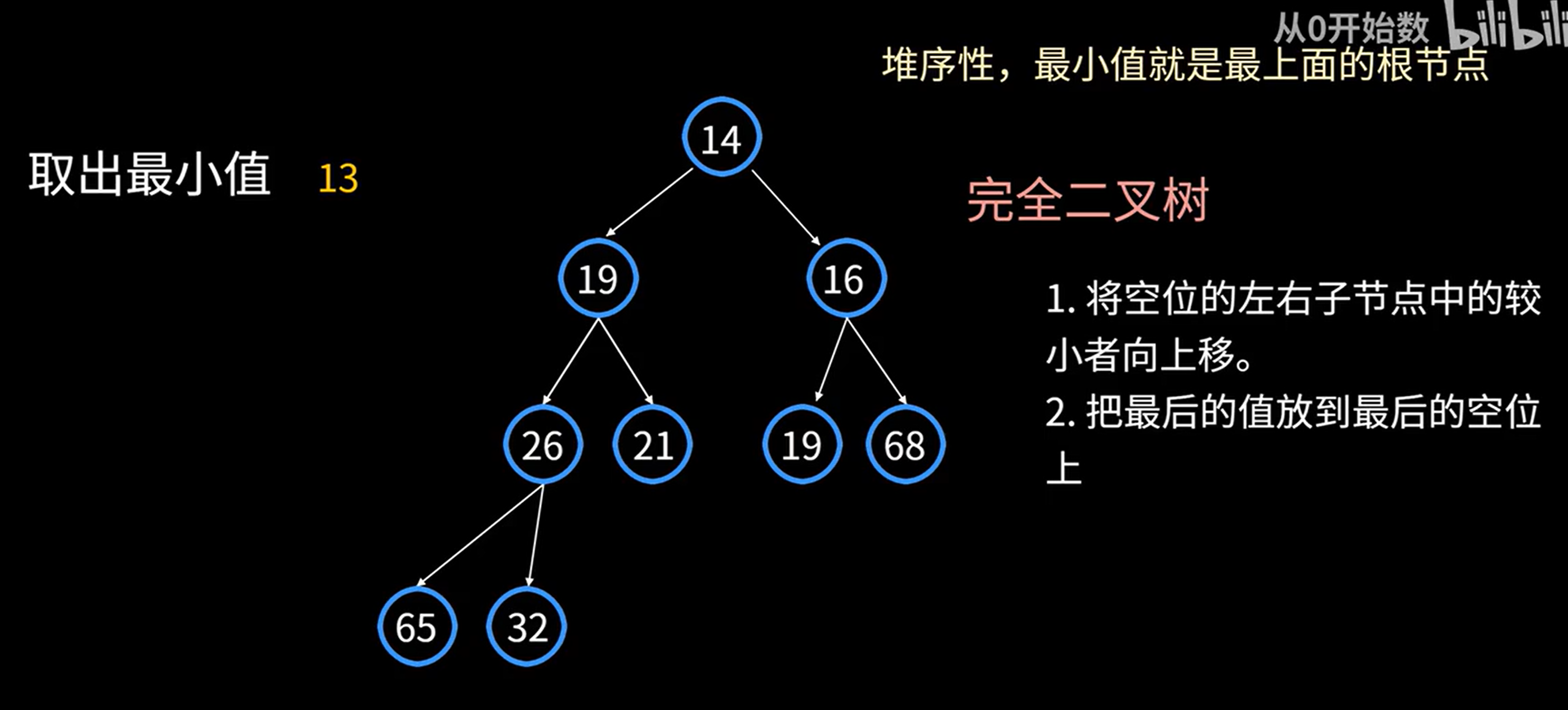
- 堆的删除元素
- 实现代码
图¶
-
图的属性:
-
边(edge):有向图/无向图、边权
-
点(vertex):出度/入度、边权
-
注:图的抽象:边就是“关系”,点就是“状态”
-
连通分量:在**无向图**中,如果两个顶点之间可以相互到达,那么就称这两个顶点连通。如果图中任意两个顶点都连通,则称为连通图;否则成为非连通图,其中,极大的连通子图为连通分量。
-
强连通分量:在**有向图**中,如果两个顶点可以各自通过一条有向路径到达另一个顶点,那么九称这两个顶点强连通。如果任意两点都强连通,则称为强连通图,否则,称为非强连通图,其中极大强连通子图为强连通分量。
-
为了叙述的方便,将连通分量和强连通分量称为**连通块**。
图的存储:¶
- 邻接表
bool graph[N][N];
//if(graph[i][j] == n) it means that i-j has an edge with the value of n
- 邻接矩阵
//usually implemented by Node List or vector
- 链式前向星¶
图的遍历:深搜(DFS)¶
1 2 3 | |
```c++
//pseudo
DFS(u) {//visit vertex u
vis[u] = true;
for(从u出发能到达的所有顶点v) {
if(vis[v] == false) {
DFS(v);
}
}
}
DFSTrave(G) {// traverse G
for(G的所有顶点u) {
if(vis[u] == false) {
DFS(u);
}
}
}
//邻接矩阵版
#define MAXV 1000
#define INF 1000000000
int n, G[MAXV][MAXV];
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
void DFS(int u, int depth) {
vis[u] = true;
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if(vis[v] == false && G[u][v] != INF) {
DFS(v,depth+1);
}
}
}
void DFSTrave() {
for(int u = 0; u < n; u++) {
if(vis[u] == false) {
DFS(u, 1);
}
}
}
//邻接表版
vector<int> adj[MAXV];
int n;
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
void DFS(int u, int depth) {
vis[u] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < adj.size(); i++) {
int v = adj[u][i];
if(vis[v] == false) {
DFS(v, depth+1);
}
}
}
void DFSTrave() {
for(int u = 0; u < n; u++) {
if(vis[u] == false) {
DFS(u,1)
}
}
}
```
图的遍历:广搜(BFS)¶
图的遍历:A^*算法¶
A*寻路算法详解 #A星 #启发式搜索_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
最小生成树 (Minimal Spanning Tree) :prim算法¶
Tree vs. Graphs
1) Trees are undirected graphs. 2) Trees do not have circles(acyclic).
So, how to turn a graph into a tree?
- Keep all the n vertices.
- Keep exactly n-1 edges.(not connected if less, has circle(s) if more.)
- It's impossible to turn a disconnected graph into a tree.
-
Definition of MST: the spanning tree with the minimum sum of weights.
-
Basic idea: grow the tree in successive stages.
- In each iteration, add one vertex and one edge to the tree.
- Thoroghout, maintain the properties of trees.
- Connectivity
- No circle
- The algorithm runs in |V| iterations.
- Maintenance:
set<int> selected[N] //place all the vertices that has alreay been linked.
set<int> unselected[N] //temporally not selected vertices
-
Procedures:
-
Update
Update all the vertices that the current vertex is connected to, if
-
Scan
-
Add
最小生成树(MST):Kruskal算法¶
单源最短路径:Dijkstra算法¶
How Dijkstra's Algorithm Works - YouTube
-
思路:可以证明,路径P_i\rightarrow ...\rightarrow P_k\rightarrow ...\rightarrow P_j的最短路径为从i到k的最短路径+从k到j的最短路径,因此要想找到从i到j的最短路径,需要依次找到到其之前各节点的最段路径。
-
维护:
- vis[n] 将所有的节点分为“已找到最短路径的节点”和“尚未找到的”,后者不断转化为前者
- dis[n] 表示在当前阶段 从源节点到i的最短路径
- fa[n] 表示这条“当前最优”的路径下i的前一个节点
- 步骤:
- 初始化(建立邻接表、初始化几个维护的数组、fa[src] = src, vis[src] = true, dis[src] = 0)
- 循环USA(for int t = 1; t < vertices.size(); i++)
- Update 更新当前节点能到达的所有尚未找到最短路径的点的最短路径(如果更短的话),这一步维护dis[n] fa[n]
- Scan 找到所有尚未找到最短路径的节点中距离最短的点
- Add 这个点的当前最段路径必为最短路径,因此将其加入“已经找到最短路径”的集合中,这一步维护 vis[n]
拓扑排序¶
Directed Acyclic Graphs(DAG) The only type of graph which has a valid topological ordering is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). These are graphs with directed edges and no cycles.
Q: How do I verify that my graph does not contain a directed cycle?
A: One method is to use Tarjan's strongly connected component algorithm which can be used to find these cycles.
拓扑排序实际上应用的是贪心算法。贪心算法简而言之:每一步最优,全局就最优。
具体到拓扑排序,每一次都从图中删除没有前驱的顶点,这里并不需要真正的做删除操作,我们可以设置一个入度数组,每一轮都输出入度为 00 的结点,并移除它、修改它指向的结点的入度(-1−1即可),依次得到的结点序列就是拓扑排序的结点序列。如果图中还有结点没有被移除,则说明“不能完成所有课程的学习”。
拓扑排序保证了每个活动(在这题中是“课程”)的所有前驱活动都排在该活动的前面,并且可以完成所有活动。拓扑排序的结果不唯一。拓扑排序还可以用于检测一个有向图是否有环。相关的概念还有 AOV 网,这里就不展开了。
算法流程:
1、在开始排序前,扫描对应的存储空间(使用邻接表),将入度为 00 的结点放入队列。
2、只要队列非空,就从队首取出入度为 00 的结点,将这个结点输出到结果集中,并且将这个结点的所有邻接结点(它指向的结点)的入度减 11,在减 11 以后,如果这个被减 11 的结点的入度为 00 ,就继续入队。
3、当队列为空的时候,检查结果集中的顶点个数是否和课程数相等即可。
思考这里为什么要使用队列?(马上就会给出答案。)
在代码具体实现的时候,除了保存入度为 0 的队列,我们还需要两个辅助的数据结构:
1、邻接表:通过结点的索引,我们能够得到这个结点的后继结点;
2、入度数组:通过结点的索引,我们能够得到指向这个结点的结点个数。
这个两个数据结构在遍历题目给出的邻边以后就可以很方便地得到。
强连通分量求法:Tarjan算法¶
[算法]轻松掌握tarjan强连通分量_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
图中是否存在环的判断¶
- 有向图:拓扑排序
- 无向图:并查集
算法¶
排序和搜索¶
二分查找¶
- 利用二分对象的**单调性**, 每次查找将查询空间折半,使得复杂度为O(logN)
- 二分的难点不在于实现,而是想到要二分,想到对谁进行二分,要利用好这个单调性。
dp¶
我们是如何确定本题可以使用动态规划来解诀的? 通常我们要从「有无后效性」进行入手分析。 如果对于某个状态,我们可以只关注状态的值,而不需要关注状态是如何转移过来的话,那么这就是一个无后效性 的问题,可以考虑使用 DP 解决。 另外一个更加实在的技巧,我们还可以通过 数据范围来猜测是不是可以用 DP 来做。 因为 DP 是一个递推的过程,因此如果数据范围是 10^{5} \sim 10^{6} 的话,可以考虑是不是可以使用一维 DP 来解决;如果 数据范围是 10^{2} \sim 10^{3} 的话,可以考虑是不是可以使用二维 DP 来做 ...
我们是如何确定本题的状态定义的? 说实话,DP 的状态定义很大程度是靠经验去猜的。 虽然大多数情况都是猜的,但也不是毫无规律,相当一部分题目的状态定义是与「结尾」或「答案」有所关联的。
DP - 路径问题 - LeetBook - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台 (leetcode-cn.com)
蓄水池抽样¶
整理题意:总的样本数量末知, 从所有样本中抽取若干个,要求每个样本被抽到的概率相等。 具体做法为: 从前往后处理每个样本, 每个样本成为答案的概率为 \frac{1}{i}, 其中 i 为样本编号 (编号从 1 开始), 最终可以确保每个样本成为答案的概率均为 \frac{1}{n} (其中 n 为样本总 数)。 容易证明该做法的正确性, 假设最终成为答案的样本编号为 k, 那么 k 成为答案的充要条件 为「在遍历到 k 时被选中」并且「遍历大于 k 的所有元素时, 均没有被选择(没有覆盖 k ) \perp 。 对应事件概率为: $$ P=\frac{1}{k} *\left(1-\frac{1}{k+1}\right) *\left(1-\frac{1}{k+2}\right) * \ldots *\left(1-\frac{1}{n}\right) $$ 首项 \frac{1}{k} 为选中 k 的概率, 后面每项分别为编号为 [k+1, n] 的样本「不被选中」的概率。 化简得: $$ P=\frac{1}{k} * \frac{k}{k+1} * \frac{k+1}{k+2} * \ldots * \frac{n-1}{n} $$ 进一步抵消化简后, 可得: $$ P=\frac{1}{n} $$ 因此, 在每一次 getrandom 时, 从前往后处理每个节点, 同时记录当前节点的编号, 当处 理到节点 k 时, 在 [0, k) 范围内进行随机, 若随机到结果为 0 (发生概率为 \frac{1}{k} ), 则将节点 k 的值存入答案, 最后一次覆盖答案的节点即为本次抽样结果。
//模板
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* head;
Solution(ListNode* _head) {
head = _head;
}
int getRandom() {
int ans = 0, idx = 0;
auto t = head;
while(t != NULL){
idx++;
if(rand() % idx == 0) ans = t->val;
t = t->next;
}
return ans;
}
};
使用蓄水池算法,用通俗的语言说一下:
- 如果我们池子中只有一个数字,那么拿到第一个数字的概率就是100%毋庸置疑。
- 两个数字50% 三个数字每个数字的几率都是33% 以此类推。。。。
当我们不知道池子里有多少个数字的时候,就需要用蓄水池的算法思想去计算。
- 当链表前行到第一个数字,此时取第一个数字的几率为100%,那result自然等于这个数字。
- 前进到第二个数字,那么此时取这个数字的几率自然就为50%(池子里只有两个数字),那么就是50%的几率取新数字,50%的几率保留原本的数字。
- 第三个数字的时候,33%的几率取当前最新的这个数字,66%的几率保留原本的数字。这66%中:原本的数字有50%的几率是1,有50%的几率是2。也就是此时三个数字的概率都为33%。 通过这个算法,就能达到取数的概率均摊,从而实现随机。
刷题记录(补充知识+做题经验)¶
二分+check¶
LC5219 每个小孩最多能分到多少糖果¶
class Solution {
public:
int maximumCandies(vector<int>& a, long long k) {
long long sum = 0;
for (int num : a)
sum += num;
/* low分得最少糖果数目,high分得最多糖果数目 */
long long low = 0, high = sum / k;
while (low != high) {
long long mid = (low + high + 1) / 2;// 二分糖果数目
long long heap = 0;// 按照每堆糖果数为mid的糖果一共可以分多少堆
/* 更新堆的个数 */
for (int num : a)
heap += num / mid;
/* 判断按当前糖果数分的对数和孩子个数进行判断 */
if (heap < k)
high = mid - 1;
else
low = mid;
}
return (int)high;
}
};
栈¶
LC150 逆波兰表达式求值¶
- 逆波兰表达式(Reverse Polish Notation)e.g.后缀表达式(Suffix Expression)
- 表达式由操作数(operand)、运算符(operator)组成,一般将运算符放在两个操作数之间,被称为(Infix Expression),如A+B。波兰数学家提出了另一种数学表示法,由两种表示形式:前缀、后缀。
- 算法:以表达式1\times(2+3)为例,维护两个栈:运算符号栈,后缀表达式输出栈。
- 首先从左至右扫描表达式,遇到操作数直接压入出栈,若读取的为操作数,则按照以下规则压入入栈。

- 整个过程分为两步:1.将中缀表达式转化为后缀表达式(利用入栈);2。逐步计算后缀表达式(利用出栈)
并查集¶
LC547 省份数量¶
经典并查集题目,有很多别名(朋友圈、城市连接问题),套模板即可:
- int findFather() //路径压缩,不做也能过,但是慢一些
- void Union()
LC1319 连通网络的操作次数¶
class Solution {
int fa[100001];
int rk[100001];
unordered_set<int> vertices;
void Union(int index_a, int index_b) {
int root_a = index_a;
while(fa[root_a] != root_a) root_a = fa[root_a];
int root_b = index_b;
while(fa[root_b] != root_b) root_b = fa[root_b];
if(root_a == root_b) return;
if(rk[root_a] == rk[root_b]) {
rk[root_a]++;
fa[root_b] = root_a;
}
else if(rk[root_a] < rk[root_b]) {
fa[root_a] = root_b;
}
else fa[root_b] = root_a;
}// union with rank
int Find(int index) {
int root = index;
while(fa[root] != root) root = fa[root];
while(index != root) {
int tmp = fa[index];
fa[index] = root;
index = tmp;
}
return root;
}//compress
void ini(int n) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fa[i] = i;
rk[i] = 1;
}
return ;
}
public:
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
int edgeSize = connections.size();
ini(n);
int cntE = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < edgeSize; i++) {
int index_a = connections[i][0];
int index_b = connections[i][1];
if(Find(index_a)!= Find(index_b)) Union(index_a, index_b);//***
else {
++cntE;
}
}
int cntV = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(vertices.find(Find(i)) == vertices.end()) {
cntV++;
vertices.insert(Find(i));
}
}
if(cntV <= cntE) return cntV;
else return -1;
}
};
注意:***处不可以写成fa[index_a] == fa[index_b],原因是在并查集中,即使在一个树中,不同子节点的根节点在Find()之前不一定是相同的!!
二叉树¶
LC889 根据前序和后序遍历构造二叉树¶
此题要求对前序、后序遍历有比较深的理解。它们都具有清晰的**递归**结构。需要注意到二叉树的前序、后序遍历**对应在数组中的结构特性**。
前序遍历数组:根节点-树的左半部分-树的右半部分
后序遍历数组:树的左半部分-树的右半部分-根节点
而”树的左/右半部分”又可以视作一棵子树,从而实现递归,直到子数组的长度为1(递归边界)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* constructFromPrePost(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode;
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
buildTree(root, preorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1, postorder, 0, 0);
return root;
}
void buildTree(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &pre, int preL, int preR, vector<int> &post, int postL, int postR) {
if(preL > preR) return ;
if(preL == preR) {//只有一个节点了
root->val = pre[preL];
return ;
}
//不止一个节点 说明至少存在一个子节点
root->val = pre[preL];
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
preL++;//preL 指向左子节点
while(postR < post.size() && post[postR] != pre[preL]) {//找到左子节点在后序中的位置,该位置前的节点都是其子节点
postR++;
}//postR - postL = 左子节点的子节点数
root->left = new TreeNode;
int preLR = preL + postR - postL;//分割点:左区间的右端点
buildTree(root->left, pre, preL, preLR, post, postL, postL);
preL = preLR + 1;//preL移动至右子节点
if(preL > preR) { //超了,说明没有右节点
return ;
}
root->right = new TreeNode;
postL = postR+1;
while(postR < post.size() && post[postR] != pre[preL]) {
postR++;
}
buildTree(root->right, pre, preL, preR, post, postL, postL);
}
};
字典树¶
LC440 字典序的第K小数字¶
算法思路
- 画出字典树
- k 表示要找到后面的第 k 个元素,起始下标是 0
- 获取以prefix开头的数字个数,包括他本身 。 如果数字个数大于 k ,下移,在prefix * 10 下的子树进行查找 。 如果数字个数小于等于 k ,右移,在prefix+1下的子树进行查找 问题的关键是求解 以prefix开头的数字个数,包括他本身
- 根节点 [prefix, prefix+1 )
- 第一层 [\operatorname{prefix} * 10,(\operatorname{prefix+1)*10)}
- 第二层 [prefix*100, \min (\mathrm{n}+1, \quad(\mathrm{prefix}+1) * 100 ))
- ...
```c++ class Solution { public: typedef long long LL; int findKthNumber(int n, int k) { int prefix = 1; k--; // k记录要找的数字在prefix后的第几个 while (k>0){ int cnt = getCnt(n, prefix); // 当前prefix 下有多少个元素;包含prefix if (cnt <= k) { // 向右 k -= cnt; prefix++; } else { // 向下 k--; prefix*=10; } } return prefix; } int getCnt(LL n, LL prefix){ LL cnt = 0; for (LL first = prefix, second = prefix+1; first<=n; first*=10, second*=10){ cnt+= min(n + 1, second) - first; } return cnt; } };
作者:muyids 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/k-th-smallest-in-lexicographical-order/solution/dfsmo-ni-jian-zhi-guo-cheng-by-muyids/ 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。 ```
图¶
出度、入度¶
LC997 找到小镇的法官¶
本题需要用到有向图中节点的==入度和出度==的概念。在有向图中,一个节点的入度是指向该节点的边的数 量;而一个节点的出度是从该节点出发的边的数量。 思胳及解法 题干描述了一个有向图。每个人是图的节点, trust 的元素 trust[i] 是图的有向边,从 trust [i][0] 指向 trust[i][1]。我们可以遍历 trust,统计每个节点的入度和出度,存储在 inDegrees 和 outDegrees 中。 根据题意,在法官存在的情况下,法官不相信任何人,每个人(除了法官外)都信任法官,且只有一名 法官。因此法官这个节点的入度是 n-1, 出度是 0 。 我们可以遍历每个节点的入度和出度,如果找到一个符合条件的节点,由于题目保证只有一个法官,我 们可以直接返回结果;如果不存在符合条件的点,则返回 -1 。
BFS¶
LC417 太平洋大西洋水流问题¶
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> P, A, ans;
int n, m;
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& M) {
n = M.size(), m = M[0].size();
P = A = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
//左右两边加上下两边出发深搜
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) dfs(M, P, i, 0), dfs(M, A, i, m - 1);
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j) dfs(M, P, 0, j), dfs(M, A, n - 1, j);
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& M, vector<vector<int>>& visited, int i, int j){
if(visited[i][j]) return;
visited[i][j] = 1;
if(P[i][j] && A[i][j]) ans.push_back({i,j});
//上下左右深搜
if(i-1 >= 0 && M[i-1][j] >= M[i][j]) dfs(M, visited, i-1, j);
if(i+1 < n && M[i+1][j] >= M[i][j]) dfs(M, visited, i+1, j);
if(j-1 >= 0 && M[i][j-1] >= M[i][j]) dfs(M, visited, i, j-1);
if(j+1 < m && M[i][j+1] >= M[i][j]) dfs(M, visited, i, j+1);
}
};
LC934 最短的桥¶
class Solution {
private:
queue<pair<int, int>> points;
vector<int> direction = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j) {
grid[i][j] = 2;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + direction[k];
int y = j + direction[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < grid.size() && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].size()) {
if (grid[x][y] == 2) continue;
if (grid[x][y] == 1) dfs(grid, x, y);
// 收集这个岛屿附近的0
if (grid[x][y] == 0) points.push({x, y});
}
}
}
public:
int shortestBridge(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
// 找到第一个岛屿
bool isFind = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (isFind) break;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
// 调用dfs把这个岛屿都标志为2
dfs(grid, i, j);
isFind = true;
break;
}
}
}
// 找另一个岛屿 BFS
int res = 0;
while (!points.empty()) {
int size = points.size();
res++;
while (size--) {
auto [x, y] = points.front();
points.pop();
// 把这一层的0全部填为2,再把外层的0再加入队列,逐层填陆地,直到碰到第二片岛屿
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int p = x + direction[k];
int q = y + direction[k + 1];
if (p >= 0 && p < m && q >= 0 && q < n) {
if (grid[p][q] == 1) return res;
if (grid[p][q] == 2) continue;
points.push({p, q});
grid[p][q] = 2;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
// 作者:carpe-diem-ew
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shortest-bridge/solution/bfs-tian-hai-zao-lu-ti-jie-si-lu-by-carp-6w8j/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
Dijkstra- Single Source Shortest Path(SSSP) algorithm¶
LC743 网络延迟时间¶
第一次实现dijskstra。总之只要记得USA就行:)
#define INF 10000000
class Solution {
bool vis[101] = {false};
int dis[101];
int fa[101];
vector<pair<int, int>> grid[101];//the path len from i to j
int size[101] = {0};
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) {//caculate all minimum path form k to else, and return the biggest
//ini
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
dis[i] = INF;
fa[i] = -1;
}
k--;
fa[k] = k;
dis[k] = 0;
vis[k] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < times.size(); i++) {
pair<int, int> temp = {times[i][1]-1, times[i][2]};
grid[times[i][0]-1].push_back(temp);
size[times[i][0]-1]++;
}
int cur = k;//the number of the point now
for(int m = 1; m < n; m++) {
for(int t = 0; t < size[cur]; t++) {
if(vis[grid[cur][t].first]) continue;
if(dis[cur] + grid[cur][t].second < dis[grid[cur][t].first]) {
dis[grid[cur][t].first] = dis[cur] + grid[cur][t].second;
fa[grid[cur][t].first] = cur;
}
}//update
int min = INF+1;
int minV;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(vis[i]) continue;
if(dis[i] < min) {
min = dis[i];
minV = i;
}
}//scan for the min unsettled v
if(min != INF) {
vis[minV] = true;
cur = minV;//update
}
}
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) return -1;
if(dis[i] > ret) ret = dis[i];
}
return ret;
}
};
哈希表¶
LC599 两个列表的最小索引总和¶
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findRestaurant(vector<string>& list1, vector<string>& list2) {
map<string, int> hashMap;
for(int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) {
hashMap[list1[i]] = i;
}
int minIndex = 100000;
vector<string> ret;
for(int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {
if(hashMap.find(list2[i]) != hashMap.end()) {
if(i + hashMap[list2[i]] < minIndex) {
ret.clear();
string tmp = list2[i];
ret.push_back(tmp);
minIndex = i + hashMap[list2[i]];
}
else if(i + hashMap[list2[i]] == minIndex) {
string tmp = list2[i];
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
dp¶
LC1575 统计所有可行路径¶
-
解析: DP - 路径问题 - LeetBook - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台 (leetcode-cn.com)
-
做题反思:
- 花了很多时间思考:什么是状态?什么是子问题?怎么写状态转移方程?
- 思考的方式就是试探,有一些想法,带进去看能不能套用动态规划
- 有一个想法:所有的点实际上分为两类,记为强点和弱点。由于距离是一维的哈密顿距离,因此将所有的点在数轴上表示,会发现例如[1,2,3],1\rightarrow3 和 1\rightarrow2\rightarrow3花费的是同样的油量。也就是说两点内部插入点,是不改边方法数的,只有新加入的点在之前点的两端才会增加油耗。然而这样想的问题在于每一次新加入的点是强点还是弱点是只取决于上一段路径的,因此需要保存上一次的路径,这样就反而变得复杂了。
- 我的状态转移的想法是:一开始只有起点和终点,然后不断加入新的点,进行状态转移。然而没有想清楚。
凸包算法¶
[计算几何]Graham算法构造凸包(重制)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
技巧¶
读题与分析¶
- 看完题意后,看题目的数据量级
-
出现O(logN) 的情形:
-
数据结构(树、堆)
- 算法(Kruskal Dijkstra 线段树)其实还是化归到数据结构,或者说利用数据结构进行优化
- 二分
- 数位运算
打表¶
two pointers¶
滑动窗口(双指针)¶
设置头尾指针,维护两指针(当然,不需要用指针这么可怕的数据类型)间满足条件的序列。 可以很容易发现,当头指针在位置x时,如果获得的最远尾指针在位置y,那么当头指针后移到x+1位置时,尾指针只会停留在原地或是继续后移。 也就是说,这是一个单向移动的过程,时间复杂度就可以简化为O(N)啦!
LC 3 无重复字符的最长字串¶
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int len = s.length();
// 对于字符串长为0时特殊处理(这里需要这么做,是因为最后答案输出时是ans + 1
if(len == 0) return 0;
//头尾下标指针初始化
int st = 0, en = 0;
int ans = 0;
bool ch[128];
// ch数组按照ASCII码的值记录每个字符是否已被使用
memset(ch, false, sizeof(ch));
// 记录第一位的字符
ch[s[0]] = true;
// 注意,因为String存储范围的下标其实是 0..(len-1),因此全部处理成en + 1 < len
while(en + 1 < len)
{
// 利用贪心,如果下一位超出String范围,或是已被使用过,则退出循环
while(en + 1 < len && !ch[s[en + 1]])
{
en ++;
ch[s[en]] = true;
}
// 由于ans存储的是尾指针-头指针的数值,因此比实际长度小1
ans = max(ans, en - st);
// 头指针后移一位
ch[s[st]] = false;
st ++;
}
// 这里使用ans + 1输出是为了将len = 1的情况一起包括进来,感兴趣的码友可以尝试一下此类数据
return ans + 1;
}
};
前缀和&差分¶
二维grid上下左右移动的小trick¶
int direction[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
int row, col;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextR = row + direction[i];
int nextC = col + direction[i+1];
}
浮点数出现精度丢失的问题¶
如果浮点数的精度有限的话,可以将浮点数\times 10 ^ n使得浮点数化成整型,如果需要输出时,只需做一次转换即可。
//浮点数的比较
if(fabs(a-b) < 1e-6) cout << "a = b" << endl;
数学基础¶
生成函数¶
生成函数:函数与数列之间的桥梁 (蒋炎岩)_bilibili
引子¶
- 多项式
- 递推公式:斐波那契数列
-
无穷小数:0.9999...
-
结论:一个生成函数里包含了一个无穷数列的每一项。
求Fibonacci 数列¶
用函数 (多项式代数) 表示各种数列¶
- c \cdot F(x) \rightarrow 数列倍增
- x \cdot F(x) \rightarrow 数列右移 (补 0 )
- [F(x)-f(0)] / x \rightarrow 数列左移
- F_{1}(x) \pm F_{2}(x) \rightarrow 数列求和/差
- F^{\prime}(x) \rightarrow 数列乘幂次 + 左移
- 导数:(c)^{\prime}=0,\\ \left(x^{n}\right)^{\prime}=n x^{n-1}
- F_{1}(x) \cdot F_{2}(x) \rightarrow 数列卷积
- F(x)\cdot {1\over{1-x}}为F(x)代表的数列的前n项和的生成函数